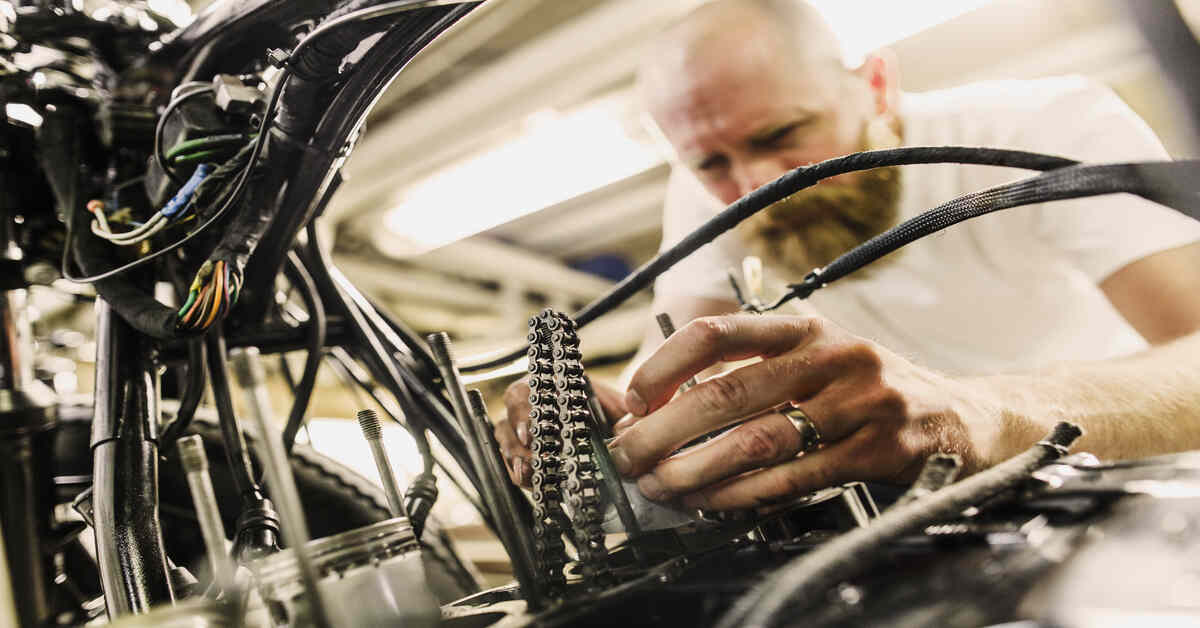
Motorcycles are complex machines and they are a blend of engineering and the excitement of speed and agility. The motorcycle mechanics art is based on motorcycle performance engineering which is the discipline that aims at improving the efficiency, power and handling of the two-wheel marvels. The post in this blog will discuss the basics of motorcycle mechanics, underline the principles of performance engineering and the way they lead to the overall experience of the ride.
The Basics of Motorcycle Mechanics
It is always important to have the fundamental parts of a motorcycle and their interaction before exploring performance engineering. A motorcycle may be divided into several systems that are critical:
- Engine: It is the core of the motorbike, the fuel is transformed into mechanical power.
- Transmission: This converts the engine to the wheels wherein one can regulate speed.
- Suspension: Cells shocks and keeps tires in touch with the road, which affects the handling and comfort.
- Brakes: These are important to the safety of the rider, as they allow him/her to slow down, or even to stop.
- Chassis: The frame which attaches all the parts together, which affects the weight and balance.
Understanding Performance Engineering
Performance engineering is the application of scientific and mathematical principles to improve the capabilities of a motorcycle. This involves optimizing design, materials, and systems to achieve maximum performance, efficiency, and reliability. In the context of motorcycles, performance engineering encompasses various aspects, including:
- Aerodynamics: The study of how air flows around and through the motorcycle. Effective aerodynamic design reduces drag and enhances stability at high speeds.
- Power-to-Weight Ratio: A critical measure of performance, this ratio compares the motorcycle’s power output to its weight. A higher ratio indicates better acceleration and handling.
- Suspension Tuning: Adjusting the suspension system to optimize ride quality and handling characteristics based on rider preferences and riding conditions.
Key Components of Performance Engineering
1. Engine Performance
The most important element of performance engineering is the engine. There are a number of strategies to improve the engine performance:
- Fuel Management Systems: Newer motorcycles have the provision of fuel injection systems where the fuel supplied is optimized depending on the needs of the engine. Dialectics of these systems can result in more power and efficiency.
- Exhaust systems: It is possible to upgrade the exhaust systems to high-performance exhaust systems, which will increase airflow, back pressure, and engine output. This is not only effective in raising horsepower but it also gives a more aggressive sound.
- Forced Induction: Turbo/superchargers force more air for massive power without size increases. See cafe racer performance tips for tuning ideas.
2. Suspension and Handling
- The suspension of a motor cycle is very crucial in the handling features of a motor cycle particularly when changing direction around corners and braking. Performance engineering concentrates upon:
- Adjustable Suspension: The adjustable forks and shocks on high-performance motorcycles allow the riders to customize their suspension to suit their performance and weight, as well as the characteristics of the roads.
- Fork and Shock Upgrades: Higher quality parts will upgrade responsiveness and give better feedback on the road and will enhance the overall riding experience.
- Distribution of weight: Weight distribution through the placement of components can be optimized to enhance handling and stability particularly when riding aggressively.
3. Braking Systems
In designing a motorcycle, the chief consideration is safety and, in this context, the performance engineering improves the braking systems to make them have a good stopping power:
- Disc Brake Upgrades: Bigger and more sophisticated disc brake systems give higher stopping power and cooling, eliminating the possibility of brake fade during hard riding.
- Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS): ABS is an anti-locking technology that enables the wheels to avoid locking up during the braking process, and thus leave the bike in a better control situation in an emergency, and it is safer without compromising performance.
4. Aerodynamics
Performance engineering relies on aerodynamics, which affects directly the speed and stability:
- Streamlined Designs: Motorcycle designers have been concerned with minimizing drag using streamlined bodywork, fairings and windshields. This provides the capability to go faster and more economically.
- Wind Tunnel Testing: Wind tunnels are commonly used by manufacturers to research the airflow, and optimize designs to perform well in aerodynamic performance.
5. Weight Reduction
The minimization of weight without reducing the structural integrity is an important objective in performance engineering:
- Lightweight Materials: The use of carbon fiber, titanium and aluminum materials can be very helpful in minimizing weight without compromising on strength. This is necessary to enhance the power to weight ratio and increase agility.
- Component Optimization: Removal of weight through streamlining of components and unnecessary parts can also minimize weight resulting in handling and acceleration improvement.
The Role of Technology in Performance Engineering
The technological development has transformed motorcycle performance engineering. The current day motorcycles feature:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Computer-aided design software enables engineers to design in three dimensions with high accuracy, which makes innovations and optimization easier in the design process.
- Data Analytics: The performance data identified through sensors and telemetry systems is able to offer insights on the behavior of a motorcycle in various conditions so that it can be improved accordingly.
- Simulation Software: Engineers can create simulations software that will result in the prediction of the impact of design changes on performance, which makes it possible to prototype and test quickly
The Future of Performance Engineering in Motorcycles
The future of performance engineering in motorcycles can be said to be optimistic as technology keeps on changing. The following are some of the trends to observe:
- Electric Motorcycles: The appearance of the electric motorcycles poses new challenges and opportunities to the performance engineering. Electric motors provide immediate torque and reduced maintenance demands that alter the performance dynamics.
- Connected Technology: With improved connectivity, motorcycles will be able to interact with the rider and other vehicles, improving the safety and performance of motorcycles with real-time data communication.
- Sustainability: With the increasing concern surrounding the environment, performance engineering will be more concerned with the development of sustainable material and technology that will minimize the carbon footprint in the production and operation of motorcycles.
Conclusion
The complexity of the motorcycle design, technology and rider experience is clearly evident in the motorcycle as an engineering science in the performance engineering industry. Motorcycle engineers manage to optimize the work of the engine, suspension, aerodynamics, and weight, which makes the splendid machines not only provide an incredible ride but also offer safety and reliability.
With the world of motorcycles still developing, it will be necessary to adopt the principles of performance engineering among the manufacturers and the fans of the sport. Whether you are a rider who needs to improve your machine or a builder who wants to work on the next great custom bike, these are the concepts that will give you the power of meeting your performance targets and enjoying the ride to the fullest.